Next: The abridged life table
Up: From a complete life
Previous: Comments on the use
To calculate health expectancies with the method of Sullivan also
implies to make some approximations on the term of life. There are two
problems:
- Because of the little sample on the 85 and beyond in the survey,
it is accustomed to calculate a single prevalence ratio for this
group age (see example of section 1.3). However on
this group age, prevalence ratios are not constant but rapidly
increasing with age.
- Often life tables are made up to age 100. Few information are
available after this age. Then, the following formulae are used:
with:
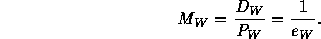
Obviously, 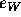 is not precisely
known [9]. More generally, quantification of mortality
above the age of 80 and evaluation of survival at these ages raise
substantial problems. A number of methodological and practical
difficulties are involved. Most important of them are methodological
and practical deficiencies of the measurement of old age
mortality. For example, errors in data play much more serious role in
the case of the elderly than in other bigger groups of the
population. Errors are present in both the death and population
statistics [5].
is not precisely
known [9]. More generally, quantification of mortality
above the age of 80 and evaluation of survival at these ages raise
substantial problems. A number of methodological and practical
difficulties are involved. Most important of them are methodological
and practical deficiencies of the measurement of old age
mortality. For example, errors in data play much more serious role in
the case of the elderly than in other bigger groups of the
population. Errors are present in both the death and population
statistics [5].
However, the biases are generally small compared to the standard
errors and can safely be ignored in most cases.
Eric Hauet
Fri Apr 25 22:40:35 DFT 1997
![]()
![]() is not precisely
known [9]. More generally, quantification of mortality
above the age of 80 and evaluation of survival at these ages raise
substantial problems. A number of methodological and practical
difficulties are involved. Most important of them are methodological
and practical deficiencies of the measurement of old age
mortality. For example, errors in data play much more serious role in
the case of the elderly than in other bigger groups of the
population. Errors are present in both the death and population
statistics [5].
is not precisely
known [9]. More generally, quantification of mortality
above the age of 80 and evaluation of survival at these ages raise
substantial problems. A number of methodological and practical
difficulties are involved. Most important of them are methodological
and practical deficiencies of the measurement of old age
mortality. For example, errors in data play much more serious role in
the case of the elderly than in other bigger groups of the
population. Errors are present in both the death and population
statistics [5].